Are reusable burs reaching their end?
Patients are the most significant stakeholders in dentistry, and their safety and hygiene are the top priorities of the dental professional. Dental procedures are reliant on the use of cutting instruments that have a working end, known as a bur. Inadequately sterilised burs are one of many causes of cross-contamination. They must be thoroughly cleaned and sterilised, but some residual microbes can remain on the burs, transmitting the infection to the next patient. For this reason, single-use burs have been introduced in the dental market, as they are pre-sterilised, packaged, and ready to use as soon as a patient sits in the dental chair.
Burs come in various materials, the most common being tungsten carbide and diamonds. Since their advent in 1897 by William and Schroeder at the University of Berlin in Germany, diamond burs have become a standard practice in dental care due to their superior sharpness, durability, and tooth-cutting properties. Burs are sterilised by steam in an autoclave and reused on several patients.
The outbreaks of HIV/AIDS (1980s) and Hepatitis C (1990s) in dental patients have reinforced the standards of cross-infection control. The Centre for Disease Control advised using general safety measures for dental treatment in 1982, including autoclaving, using ETOX, or chemically sterilising dental instruments after each use.
Though these sterilisation measures are effective, they are tedious, time-consuming, and require expensive equipment. Some hardy microbes can still be found even after following strict sterilisation protocols, which can lead to cross-contamination.
Additionally, patients cannot be certain that their dentist has properly sterilised the burs, which raises severe questions regarding the safety of reusing burs.
Reusable diamond burs become less efficient at cutting after being used on numerous patients, which can cause pain and discomfort during cavity preparation and require more time than a fresh, sharper bur.
Due to these issues with bur dullness, sterility, and particularly inadequate cross-infection control, single-use burs were introduced in the early 1990s. They became popular when the CDC recommended that single-use burs be used whenever possible as they limit infection transmission, particularly to and from immunocompromised patients.
The rising popularity of Single-Use burs
The ever-increasing patient load in dental practices pushes dentists to streamline their workflow. Washing, packing, sterilising, and reusing dental instruments, especially burs, are major hindrances in the workflow.
Pre-sterilised single-use burs packed in individual pop-up blisters are a promising solution for dental practices to improve their workflow. These single-use burs are ready to use immediately, eliminating the misery of waiting for the sterilisation cycle to end or for the instruments to cool down.
Even when autoclaved, reusable burs are not 100 per cent sterile. Concerns for cross-infection control led researchers to develop single-use burs. Moreover, the pop-out sound of the new single-use bur reminds the patient that the procedure will be germ-free.
Traditional reusable burs tend to dull after multiple cycles of use and autoclaving. As the bur dulls, it becomes less effective in cutting, taking much longer and causing greater discomfort to the patient. As the name suggests, single-use burs are only used once in their sharp new form and thus don’t dull, making the operation much more pleasant for both the operator and the patients.
Single-use burs have thus introduced a new level of patient comfort and quality of dental work. Patients are now more satisfied with the dental experience; according to research published in the Journal of American Dental Association in 2018, patients treated with a single-use bur were more content as they experienced less pain, increased comfort, and greater overall satisfaction. [2]
Dentists are also happy using sterile single-use burs that provide an efficient cutting experience. According to a study published in the Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice in 2020, 90% of Dentists that used single-use burs were content with their use and would recommend them to fellow dentists. [3]
Reusable Diamond burs, as the name suggests, are also quite expensive compared to single-use burs.
Single-use Burs in Australia: a look at the Local Perspective
Like the rest of the world, Australian dentists recognise the value of single-use burs in modern dental practice. Research suggests that an increasing number of Australian dentists are utilising these burs, discarding them after a single use.
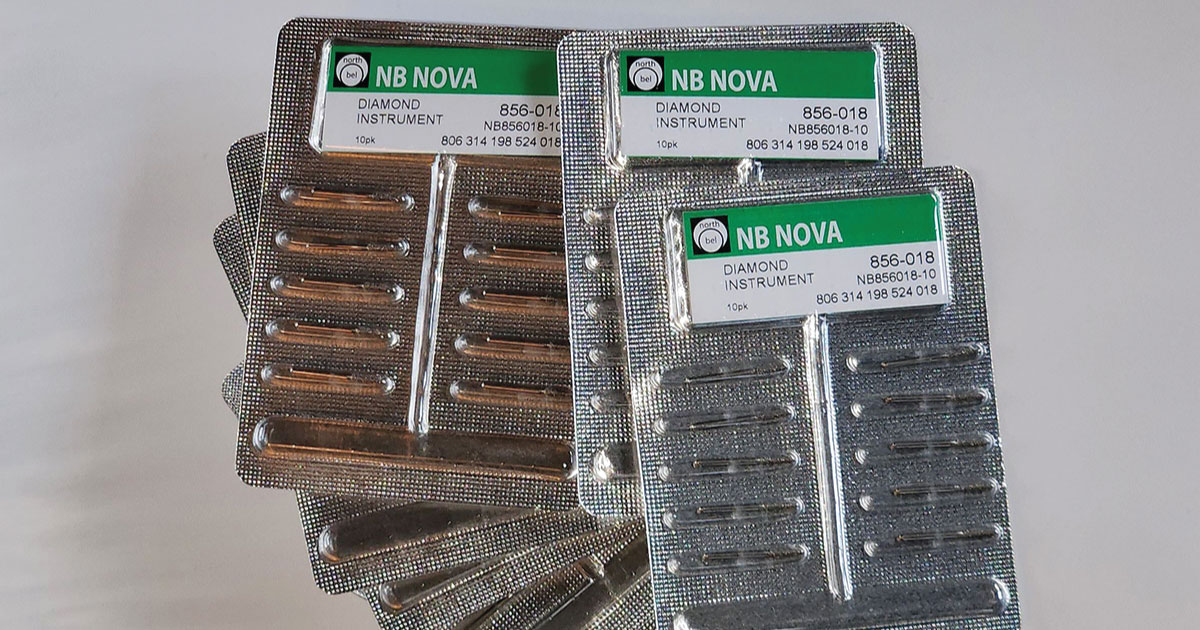
Considering this need for modern Australian dental practices, Norlin Dental offers NB NOVA single-use diamond burs at an extraordinarily low price. They are manufactured according to the ISO international standards. NB NOVA single-use burs are designed with a single layer of geometrically cut diamond pieces embedded in a layer of chromium that provide a sharp cutting edge for the enamel or dentine surface while minimising pain and discomfort for the patient. The chromium layer gives the bur anti-friction properties, preventing heat buildup and thermal damage to the pulp.
Scanning Electron Microscope analysis reveals that NB NOVA has better abrasive action than a standard bur due to a reduced bonding layer and enhanced diamond grain exposure, allowing for debris removal. This results in an extremely efficient cutting.
For the dentist, it means reaping the benefits of a new bur every time. The luxury of a new bur, such as the convenience of a consistent hand position for efficient cutting, becomes a normal routine with these burs. The clinic’s cost is also dramatically reduced as these burs are pocket- and handpiece-friendly. Dental turbines have a longer lifespan thanks to optimal dimensional tolerances.
NB NOVA: multiple designs fit for many clinical applications
Every clinical procedure in dentistry requires a specific instrument due to the anatomy of anterior and posterior teeth and various tooth preparations like Inlays, onlays, Crowns & Bridges. Considering this, NB NOVA has designed multiple burs with different shapes according to ISO standards.
Amalgam & Composites
Amalgam has been the pioneer of filling materials in dentistry. In the most common Class I &I I cavities, Amalgam has specific requirements to resist occlusal forces and retain itself in the cavity. NB NOVA single-use round burs are recommended according to the ISO 801 code for initial entry into the cavity.
Amalgam is retained in the cavity by preparing the vertical walls to converge occlusal. The NB NOVA Inverted Cone Bur and pear-shaped bur are recommended for this cavity feature, as their inherent shape automatically creates the desired cavity configuration.
Although a composite requires no specific cavity shape, a standardised preparation enhances its retention in larger cavities.
Inlays and Onlays
Inlays and onlays are prepared outside the patient’s mouth (in the dental laboratory). Precise cavity preparations are necessary for Inlays and onlays to cement into place, and NB NOVA burs ensure that. Initial entry is done with a round bur, as with Amalgam and Composites.
The recommended football or wheel-shaped bur performs occlusal and lingual reductions. The flat and round-end cylinder completes basic cavity preparations shaped NB NOVA single-use burs. Using Tapered and Needle End Flame shaped burs creates a flawless finish.
Crown & Bridge
More extensively damaged teeth are restored by placing a crown. Bridges, on the other hand, replace a missing tooth by using adjacent healthy teeth as support. Like the previously mentioned restorations, crowns and bridges have exact cavity protocols to ensure optimal resistance and retention.
Similar burs are recommended, like round for initial entry and football for occlusal reduction. However, crown and bridge preparations cover an additional surface, the cervical margin of the tooth. NB NOVA Tapered Flame Bur is recommended to prepare fine chamfer margins, whereas Needle End Flame Bur is optimum for knife edge margins.
Dental Veneers and Laminates
Dental Veneers are a thin coating of restorative material placed on the labial surface of anterior teeth by removing a thin layer of enamel. They are employed mainly as aesthetic procedures to improve the appearance of a patient’s smile by hiding any discolouration or trauma.
Enamel reduction from the facial and Incisal surfaces are the main steps in tooth preparation for Veneers. NB NOVA burs are available in four shapes: round-end taper, needle-end flame, round-end cylinder and bevelled cylinder. The tapered flame-shaped NB NOVA burs prepare the fine subgingival margin to provide an invisible finish line.
Conclusion
In conclusion, single-use burs are a great innovation in dentistry that ensures patient safety and hygiene while ensuring efficient and economical oral healthcare delivery. NB NOVA has revolutionised this use by providing this advancement in an extraordinarily low price. Order directly from www.norlindental.com.au. So don’t wait around – Get your single-use burs today, save a tooth or two, and keep the patient safe and satisfied!
References:
https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/infectioncontrol/pdf/recommendations-excerpt.pdf
Patient satisfaction with single-use versus reusable dental burs: A randomised controlled trial. Mills, S. E., Daw, K., & Smith, A. M. (2018). Journal of the American Dental Association, 149(1), 31-38. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29269091/